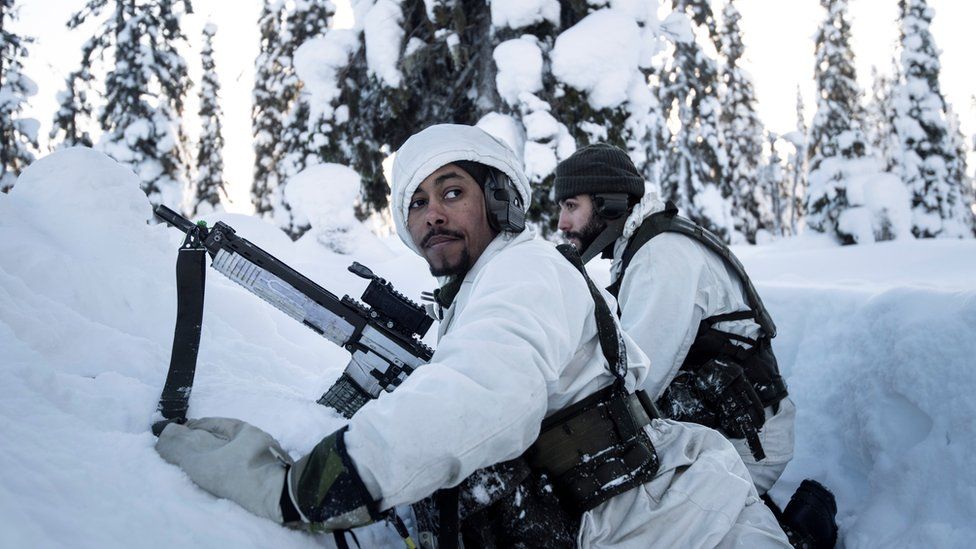
Finland and Sweden can obtain Nato subscription within days – a huge change for 2 countries with a lengthy history of wartime neutrality as well as staying out of military partnerships.
Russia strongly opposes the two states joining as well as makes use of the development of the West’s protective armed forces alliance as a pretense for its war in Ukraine.
If they do, it will end over 200 years of Swedish non-alignment. Finland adopted nonpartisanship following a bitter defeat by the Soviet Union during World Battle Two.
Finnish public support for signing up with Nato was for many years at around 20-25%. But considering that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, it has actually skyrocketed to a record high of 76%, according to the current viewpoint survey. In Sweden, 57% of the population want to join, once more much higher than prior to the battle.
Decision time
Finnish President Sauli Niinisto will lay out his position on Nato on Thursday, and also the ruling events of both nations will state what they think over the weekend.
If it is an indeed, both parliaments will have clear bulks in favour of subscription, as well as the application procedure can begin.
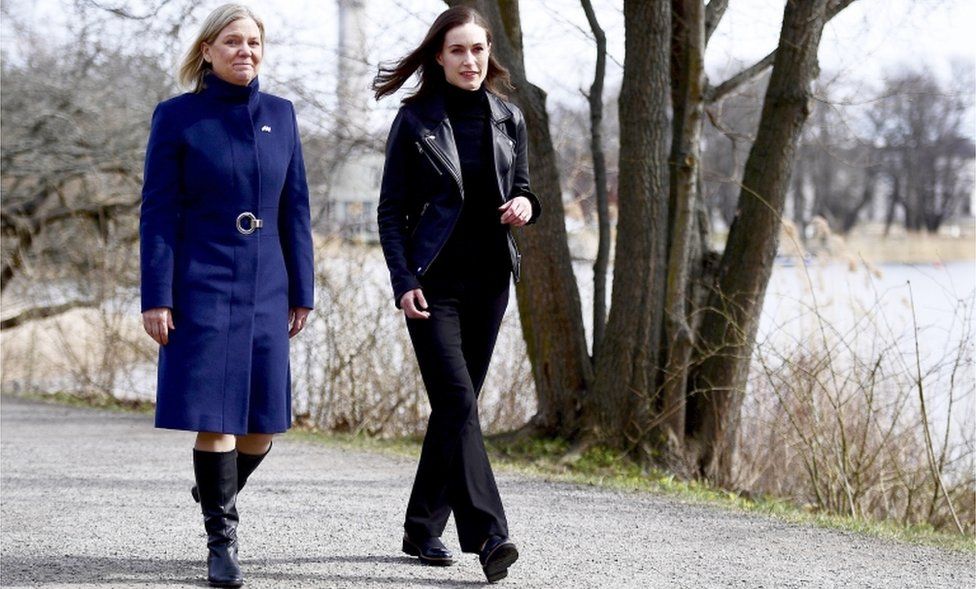 While the Finnish Social Democrats are likely to be in favour, Sweden’s Social Democrats have been divided on the problem, as well as are presently holding an inner appointment. Nevertheless celebration Nato-sceptics appear to be leaning in the direction of joining. “Whatever appears to be entering that direction,” claims ex-Foreign Preacher Margot Wallstrom.
While the Finnish Social Democrats are likely to be in favour, Sweden’s Social Democrats have been divided on the problem, as well as are presently holding an inner appointment. Nevertheless celebration Nato-sceptics appear to be leaning in the direction of joining. “Whatever appears to be entering that direction,” claims ex-Foreign Preacher Margot Wallstrom.
The United States claims it is certain it can address any kind of safety issues either nation might have in the period between applying and formally becoming members. UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson visits both countries on Wednesday as well as will review their “broader safety problems”.
Why join now?
Finnish ex-Prime Minister Alexander Stubb says signing up with the partnership was a “done offer” for his nation as soon as Russian soldiers attacked Ukraine on 24 February.
Swedish Support Minister Peter Hultqvist explains that day as the minute the Russian leader showed he was “unforeseeable, undependable and prepared to income a vicious, bloody as well as ruthless war”. After guaranteeing Sweden would certainly never join Nato last November, he currently talks of the Nordic region’s supports being strengthened if both countries sign up.
Eventually, numerous Finns and Swedes are aiming to Nato in the idea it will certainly maintain them secure in an unpredictable Europe.
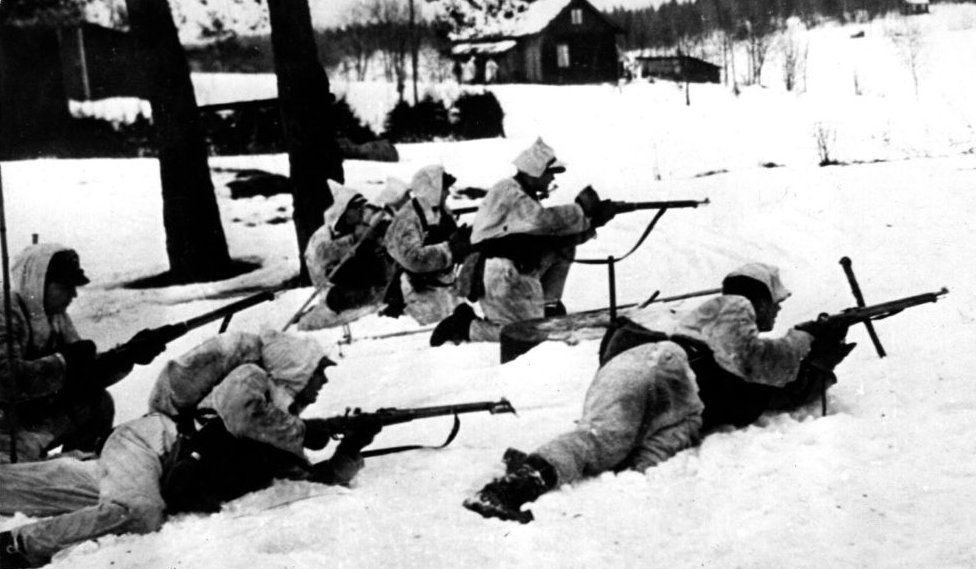 For Finns, occasions in Ukraine bring a haunting feeling of familiarity. The Soviets attacked Finland in late 1939. For greater than 3 months the Finnish army put up tough resistance, in spite of being heavily surpassed.
For Finns, occasions in Ukraine bring a haunting feeling of familiarity. The Soviets attacked Finland in late 1939. For greater than 3 months the Finnish army put up tough resistance, in spite of being heavily surpassed.
They stayed clear of occupation, however wound up shedding 10% of their area.
Enjoying the battle in Ukraine unfold is like reliving this background, says Iro Sarkka, a political researcher at the College of Helsinki. Finns are taking a look at their 1,340 km (830 mile) boundary with Russia, she claims, and also reasoning: “Could this take place to us?”
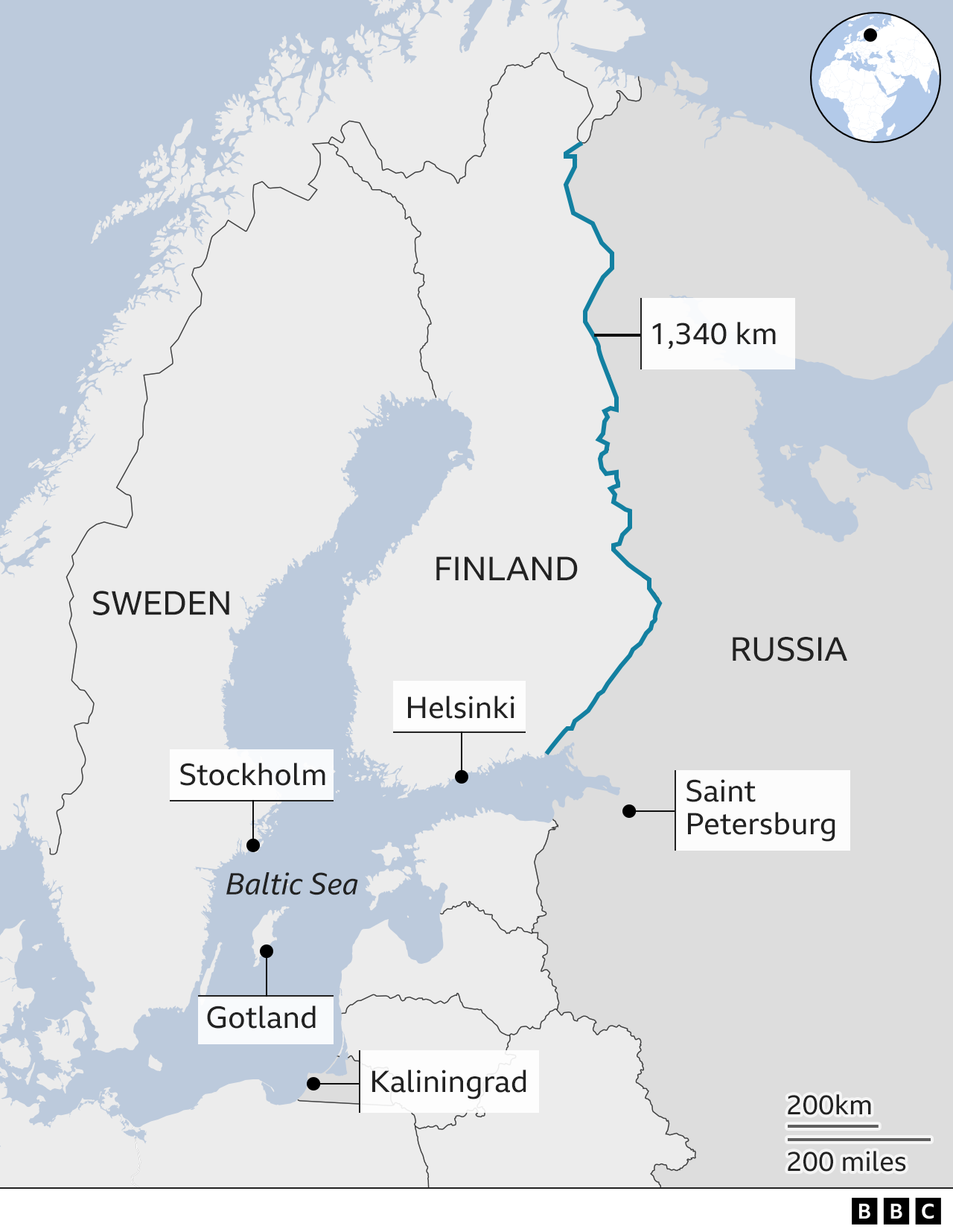 Sweden has actually also felt endangered in the last few years, with a number of reported airspace offenses by Russian armed forces airplane.
Sweden has actually also felt endangered in the last few years, with a number of reported airspace offenses by Russian armed forces airplane.
In 2014, Swedes were transfixed by reports that a Russian submarine was hiding in the shallow waters of the Stockholm island chain.
Two year later Sweden’s military returned to the tiny yet strategically essential Baltic Sea island of Gotland, after abandoning it for two decades.
What would change?
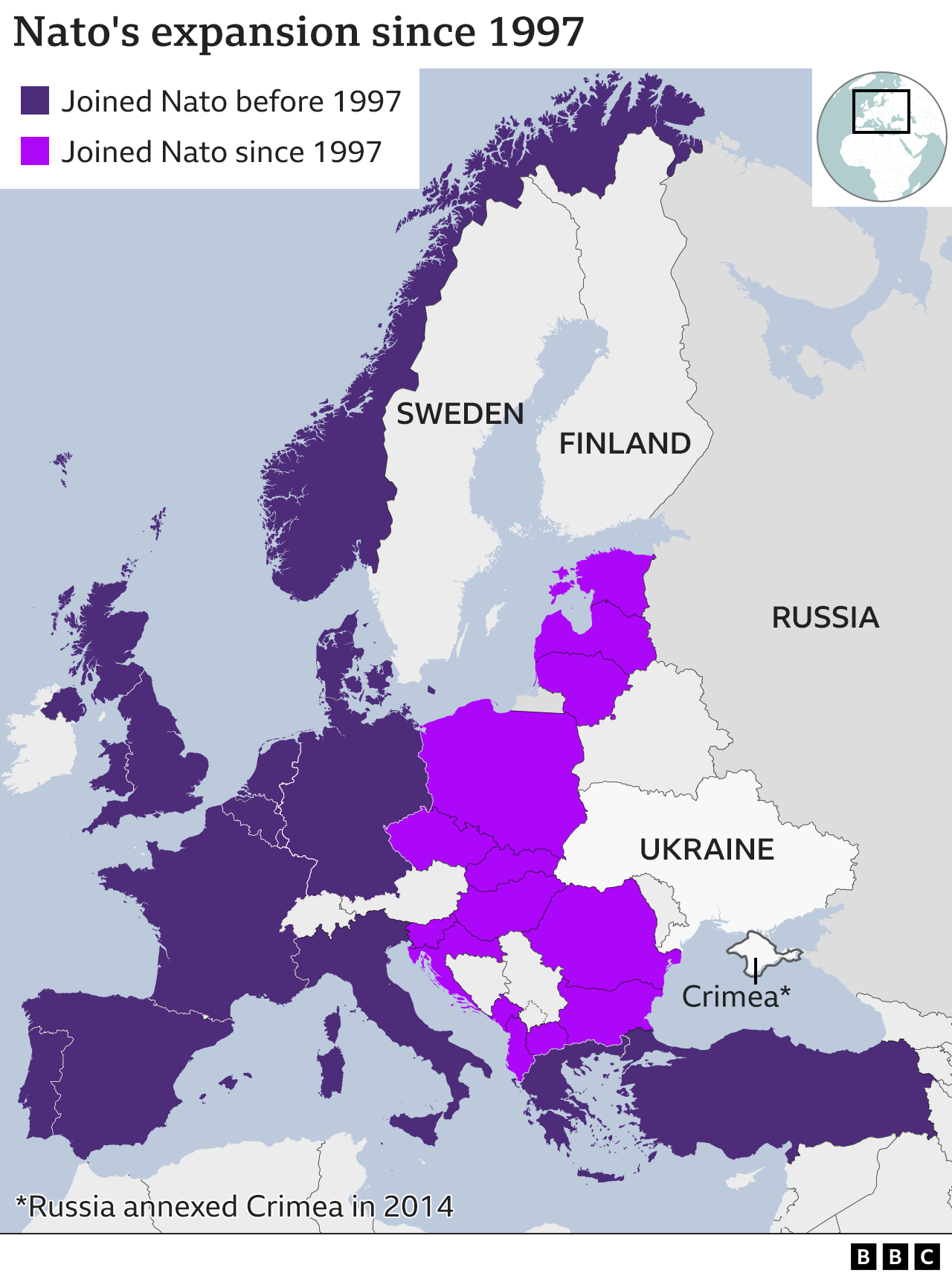
Somehow, not much. Sweden as well as Finland ended up being main companions of Nato in 1994 and have actually since ended up being significant contributors to the alliance. They have actually participated in several Nato objectives since completion of the Cold Battle.
A significant change would be the application of Nato’s “Short article 5”, which watches a strike on one participant state as an attack on all. For the very first time, Finland and also Sweden would have protection guarantees from nuclear states.
Although the debate has actually changed in favour of membership very rapidly in both countries, chronicler Henrik Meinander suggests Finland was mentally ready for it. Small actions towards Nato have actually progressively been taken considering that the autumn of the Soviet Union, he claims.
In 1992, Helsinki purchased 64 United States battle aircrafts. Three years later, it signed up with the European Union, together with Sweden. Every Finnish federal government since then has assessed the supposed Nato choice, he claims. The military, which offers a populace of 5.5 million, has a wartime strength of 280,000 soldiers, as well as in total 900,000 reservists.
Sweden took a different course in the 1990s, decreasing the size of its armed forces and also transforming concerns from territorial defence to peacekeeping objectives around the world. But that all changed in 2014, when Russia linked Crimea from Ukraine. Conscription returned and also protection costs was increased. In 2018, every family received army handouts qualified If crisis or war comes – the very first time they were sent out since 1991.
Finland has actually currently gotten to Nato’s agreed protection investing target of 2% of GDP, and Sweden has actually drawn up plans to do so.
- Johnson to hold Ukraine talks with Sweden and also Finland
- Is Nato’s Nordic expansion a threat or increase to Europe?
- What is Nato as well as could Finland and also Sweden join?
What are the risks?
Head of state Putin has actually often utilized the possibility of Nato increasing to Ukraine to justify his intrusion. So Sweden and also Finland joining the alliance would certainly be perceived as a justification.
Russia’s foreign ministry says both nations have actually been warned of the “repercussions” of such a step. Dmitry Medvedev, a close ally of the Russian leader, has warned that Nato accession might trigger Moscow to release nuclear tools in Kaliningrad, the Russian exclave between Poland and Lithuania.
While not disregarding these risks, Alexander Stubb suggests an extra reasonable risk is of Russian cyber strikes, disinformation projects and occasional airspace offenses.
Would certainly Nato make Sweden and also Finland much safer?
There is a substantial minority, at least in Sweden, who think it would certainly not.
Deborah Solomon, from the Swedish Peace and also Settlement Culture, says that Nato’s nuclear prevention increases tensions and threats an arms race with Russia. This makes complex peace initiatives, she says, and also makes Sweden a less safe place.
An additional anxiety is that in signing up with the alliance, Sweden would certainly lose its leading function in global nuclear disarmament initiatives. Margot Wallstrom recalls how some Nato international preachers were greatly pressed by the US not to participate in UN disarmament arrangements in 2019.
But Mr Hultqvist, the present protection preacher, preserves there is no opposition in between Nato membership and also Sweden’s disarmament aspirations.
Much of Sweden’s Nato-sceptics recall to the 1960s-80s, when Sweden utilized its nonpartisanship to place itself as a worldwide conciliator as well as ally to the colonized world. It vocally criticised the Soviet Union as well as US, as well as says at one point in the 1970s it was the only Western country to sustain South Africa’s anti-apartheid activity.
If Sweden signs up with Nato, it would be “abandoning the desire” of being an arbitrator, Ms Solomon claims.
Finland’s nonpartisanship was extremely different. It transpired as a condition of tranquility imposed by the Soviet Union in a 1948 “relationship contract”. It was seen as a pragmatic way of enduring and also keeping the nation’s freedom.
Sweden’s nonpartisanship was a matter of identification as well as ideology, whereas in Finland it was a question of existence, says Henrik Meinander. Part of the reason Sweden can also manage to have a dispute regarding Nato membership is due to the fact that it utilizes Finland and the Baltics as a “barrier area”, he thinks.
Finland deserted its neutrality after the Soviet Union fell down. It sought to the West and looked for to totally free itself from the Soviet sphere of impact. Joining the European Union was viewed as offering not only economic benefits yet protection advantages too.
Iro Sarkka suggests joining Nato was viewed as too huge a step for Finland to take in the very early 1990s, having simply arised from nonpartisanship.
But times as well as assumptions of risk have altered. Currently, a lot of Finns say they prepare.
Disclaimer: TheWorldsTimes (TWT) claims no credit for images featured on our blog site unless otherwise noted. The content used is copyrighted to its respectful owners and authors also we have given the resource link to the original sources whenever possible. If you still think that we have missed something, you can email us directly at theworldstimes@gmail.com and we will be removing that promptly. If you own the rights to any of the images and do not wish them to appear on TheWorldsTimes, please contact us and they will be promptly removed. We believe in providing proper attribution to the original author, artist, or photographer.
Resources: BBC
Last Updated: 11 May 2022






























































